
public class CountRMIClient
{ public static void main(String args[])
{ // Create and install the security manager
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager());
try
{ CountRMI myCount = (CountRMI)Naming.lookup("rmi://"
+ args[0] + "/" + "my CountRMI");
// Set Sum to initial value of 0
System.out.println("Setting Sum
to 0");
myCount.sum(0);
// Calculate Start time
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Increment 1000 times
System.out.println("Incrementing");
for (int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; i++
)
{ myCount.increment();
}
// Calculate stop time; print out
statistics
long stopTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Avg Ping = "
+ ((stopTime - startTime)/1000f)
+ " msecs");
System.out.println("Sum = " + myCount.sum());
} catch(Exception e)
{ System.err.println("System Exception" + e);
}
System.exit(0);
}
}
public class CountRMIServer
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Create and install the security manager
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager());
try
{
// Create CountRMIImpl
CountRMIImpl myCount = new CountRMIImpl("my
CountRMI");
System.out.println("CountRMI Server ready.");
} catch (Exception e)
{ System.out.println("Exception: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
The server does not terminate, because the object is used by the RMI runtime in a thread. This behavior is inherited from UnicastRemoteObject.
public class CountRMIImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject
implements CountRMI
{
private int sum;
public CountRMIImpl(String name) throws RemoteException
{
super();
try
{
Naming.rebind(name, this);
sum = 0;
} catch (Exception e)
{ System.out.println("Exception: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public int sum() throws RemoteException
{ return sum;
}
public void sum(int val) throws RemoteException
{ sum = val;
}
public int increment() throws RemoteException
{ sum++;
return sum;
}
}
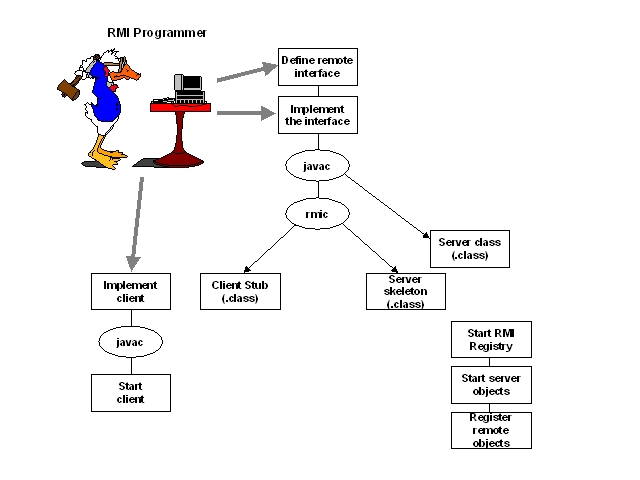
The last command creates a stub CountRMI_stub.class and a skeleton CountRMI_Skel.class.
In VisualAge, the proxies can be created from a menu entry. Select the implementation file (CountRMIImpl) and follow the following sequence in cascading menus:
Selected->Tools->Remote Method Invocation->Generate proxies
Under Winodws, the following commands will do the trick:
DOS prompt> start rmiregistry
DOS prompt> start java CountRMIServer
DOS prompt> java countRMIClient serverHost
If you are running the registry on the same computer, then use localhost as the name of the host.
Under UNIX, the scenario is similar:
UNIX prompt> rmiregistry &
UNIX prompt> java CountRMIServer &
UNIX prompt> java countRMIClient serverHost
Make sure that the PATH includes the java binary directory (so rmiregistry
and java can be found).